Public Transit Accessibility for People with Disabilities
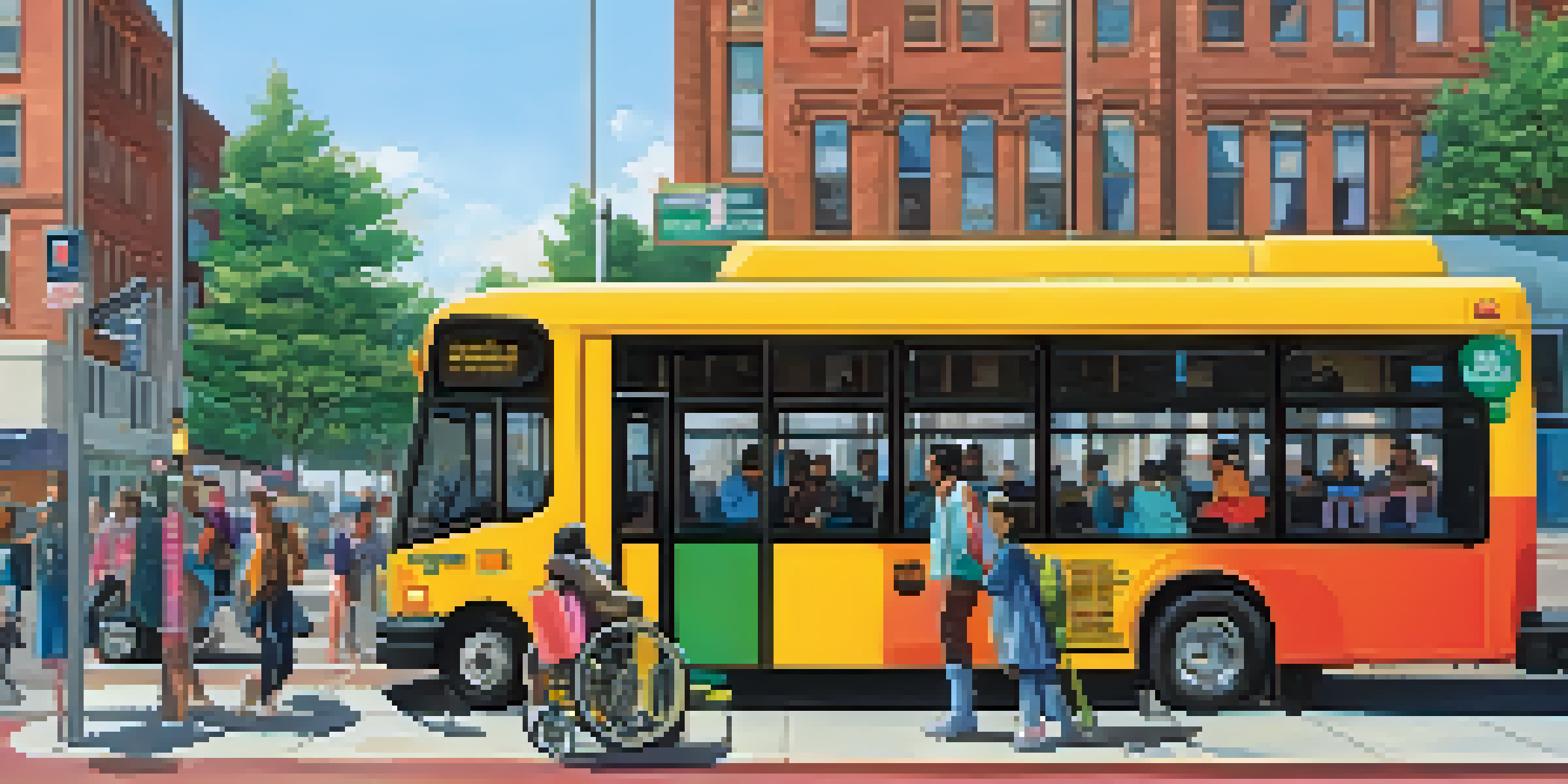
Understanding the Importance of Public Transit Accessibility
Public transit serves as a lifeline for many individuals, especially those with disabilities. It offers essential mobility that allows people to access jobs, education, and healthcare. Without accessible transit options, these individuals may face isolation and limited opportunities.
Public transportation is not just a means of getting from one place to another; it is a vital link to opportunity.
Enhancing accessibility is not just about compliance with regulations; it's about fostering an inclusive society. When public transit is accessible, it empowers people with disabilities to participate fully in their communities. This inclusivity benefits everyone, creating a richer, more diverse environment.
Moreover, accessible public transit can stimulate local economies. When individuals can travel freely, they are more likely to shop, dine, and engage with local businesses. This economic boost is a compelling reason for cities to prioritize accessibility in their transit planning.
Common Barriers to Public Transit Accessibility
Despite advances in technology and design, many public transit systems still present barriers for individuals with disabilities. These barriers can include inaccessible vehicles, inadequate information, and poorly designed facilities. For example, a lack of ramps or elevators at train stations can make it impossible for someone in a wheelchair to board.
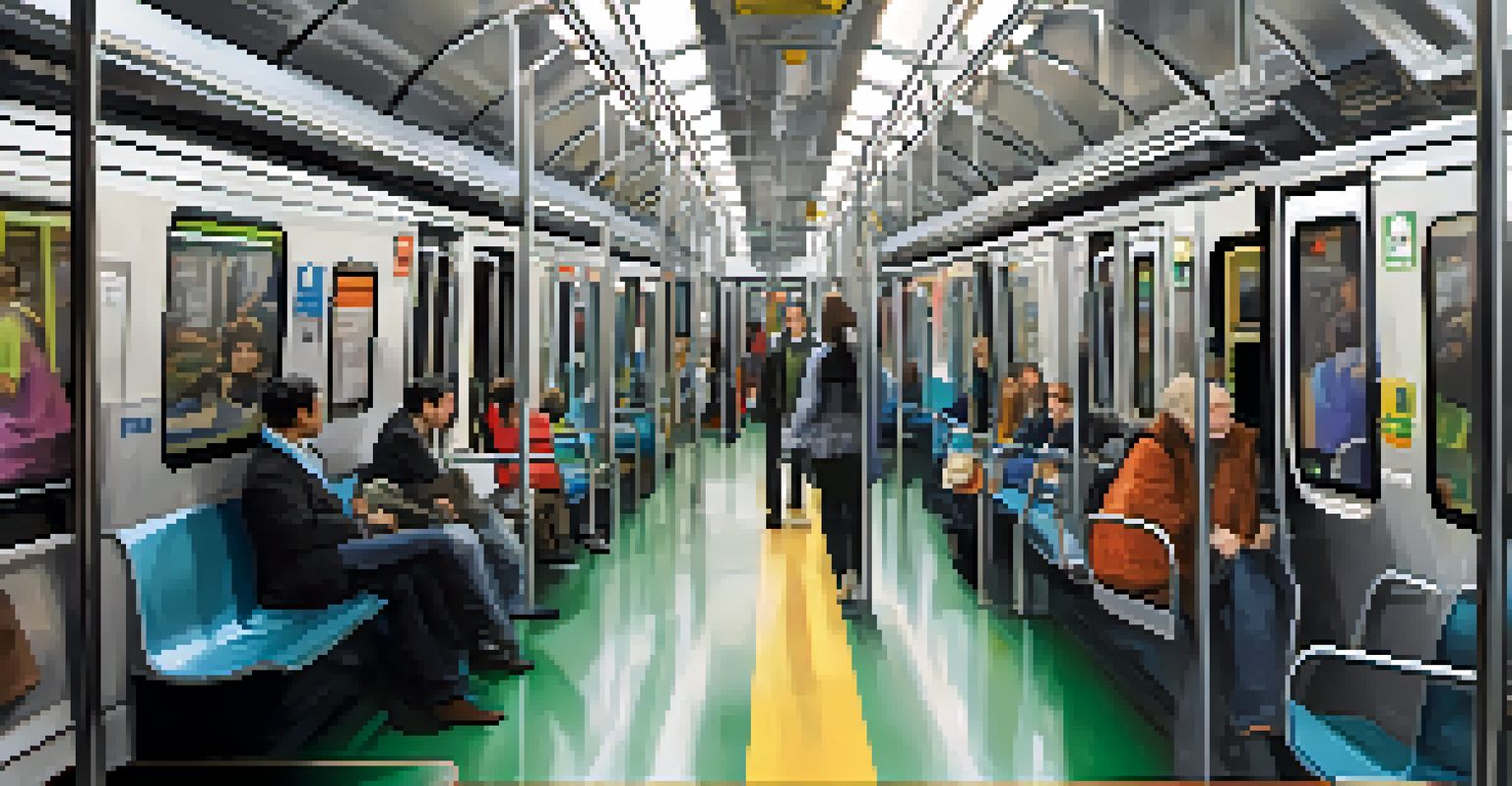

Additionally, the absence of audible or visual announcements can hinder those with hearing or vision impairments. If a transit system does not provide clear information about routes and schedules, it can create confusion and frustration. These challenges highlight the need for more comprehensive solutions.
Public Transit Empowers Communities
Accessible public transit enables individuals with disabilities to engage fully in their communities, enhancing inclusivity for all.
Moreover, the perception of public transit as unsafe or unreliable can deter people with disabilities from using it. Fear of negative experiences, such as being treated poorly or facing harassment, can lead to further isolation. Addressing these concerns is crucial to encourage greater use of public transit.
Legislation Supporting Accessibility in Public Transit
Many countries have implemented legislation aimed at improving accessibility in public transit. For instance, the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) mandates that public transport systems must be accessible to individuals with disabilities. This law has driven significant changes across the United States, leading to improved facilities and services.
Accessibility is not a privilege, but a right for all individuals in society.
In addition to the ADA, various local and state regulations also support accessibility initiatives. These laws often require transit agencies to conduct regular assessments and make necessary modifications. This proactive approach ensures that accessibility remains a priority.
However, legislation alone is not enough. Ongoing monitoring and enforcement are essential to ensure compliance. Communities must also advocate for their rights, pushing for necessary changes and improvements in their local transit systems.
Innovative Solutions for Improving Transit Accessibility
As technology evolves, so do the solutions for enhancing public transit accessibility. For example, mobile apps can provide real-time information about transit options and accessibility features. These tools can empower users to plan their trips more effectively and with confidence.
Additionally, many transit agencies are exploring partnerships with rideshare companies to offer accessible transportation options. This collaboration can fill gaps in service and provide more flexible solutions for individuals with disabilities. By integrating different modes of transport, cities can create a more seamless experience.
Barriers Still Limit Accessibility
Despite improvements, many public transit systems still face significant barriers that hinder access for individuals with disabilities.
Moreover, community involvement plays a vital role in developing innovative solutions. Engaging with people who rely on public transit can provide valuable insights into their needs and preferences. This feedback can guide agencies in making informed decisions about accessibility improvements.
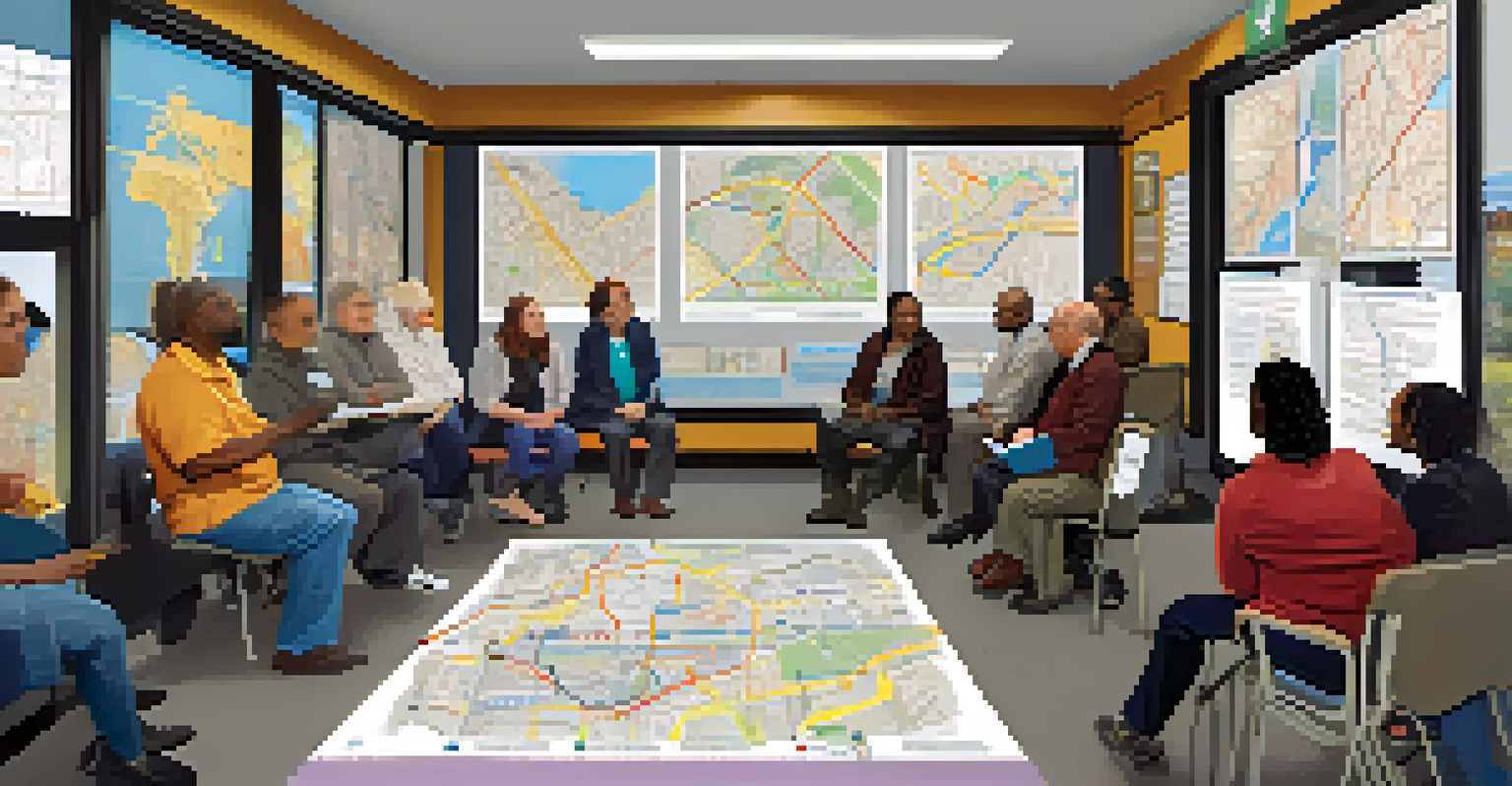
The Role of Community Engagement in Accessibility Efforts
Community engagement is fundamental in identifying the specific needs of individuals with disabilities regarding public transit. When transit agencies actively involve community members in the planning process, they can design services that truly reflect user needs. For instance, conducting surveys or focus groups can uncover valuable insights.
Furthermore, building relationships with advocacy groups can amplify the voices of those who face accessibility challenges. These organizations often have extensive knowledge and experience that can inform transit improvements. Collaborating with them can lead to more effective and inclusive solutions.
Ultimately, fostering an ongoing dialogue between transit agencies and the communities they serve is essential. Regular feedback loops can help agencies adapt and respond to changing needs, ensuring that accessibility initiatives remain relevant and effective.
Case Studies of Successful Accessible Transit Programs
Examining successful accessible transit programs can provide valuable lessons for other cities. For example, the city of San Francisco has made significant strides in creating an inclusive transit system. Their efforts include the implementation of low-floor buses and comprehensive training for staff on disability awareness.
Another notable example is London, which has invested heavily in making its Underground system more accessible. From step-free access at stations to audio-visual information on trains, these enhancements have transformed the travel experience for individuals with disabilities. These investments show that commitment can lead to remarkable improvements.
Legislation Drives Transit Improvements
Laws like the ADA have led to critical advancements in public transit accessibility, but ongoing advocacy and enforcement are essential for continued progress.
These case studies not only highlight successful practices but also inspire other cities to follow suit. By learning from these examples, transit agencies can adopt best practices and tailor them to fit their unique contexts.
Future Directions for Public Transit Accessibility
Looking ahead, the future of public transit accessibility will likely involve more advanced technology and innovative design. The integration of smart technology, such as AI and IoT, can enhance user experience and streamline services. Imagine a world where public transit adapts in real-time based on the needs of its users!
Moreover, there is a growing emphasis on universal design principles, which aim to create spaces that are inherently accessible to everyone. This approach not only benefits individuals with disabilities but also enhances the overall experience for all users. A well-designed transit system should be intuitive and accommodating.

Ultimately, the goal is to create a public transit system that is not only accessible but also welcoming. As cities continue to evolve, prioritizing accessibility will be key to fostering inclusivity and enhancing the quality of life for all residents.